
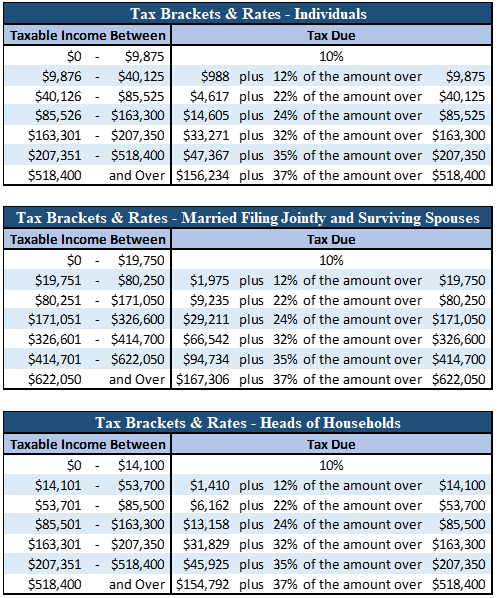
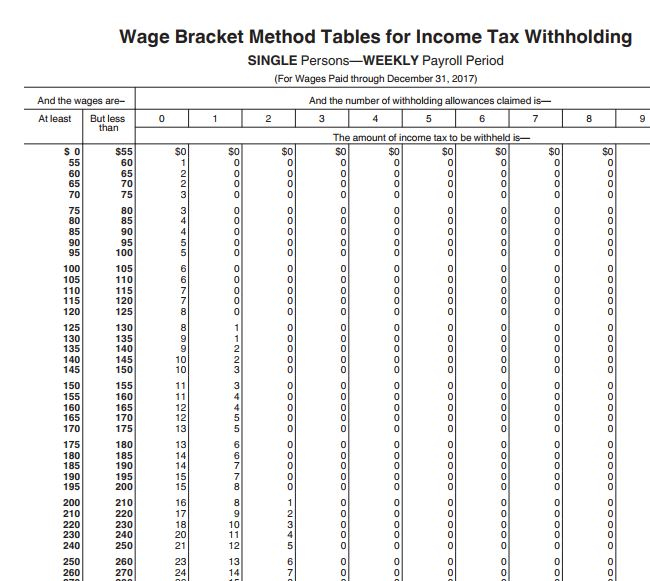
#Irs 2020 federal tax tables plus#
Don't include any social security benefits unless (a) you are married filing separately and you lived with your spouse at any time in 2022, or (b) one-half of your social security benefits plus your other gross income and any tax-exempt interest is more than $25,000 ($32,000* if married filing jointly). But, in figuring gross income, don't reduce your income by any losses, including any loss on Schedule C, line 7, or Schedule F, line 9. Gross income from a business means, for example, the amount on Schedule C, line 7, or Schedule F, line 9. It also includes gains, but not losses, reported on Form 8949 or Schedule D. Gross income means all income you receive in the form of money, goods, property, and services that isn't exempt from tax, including any income from sources outside the United States or from the sale of your main home (even if you can exclude part or all of it). (If your spouse died in 2022 or if you are preparing a return for someone who died in 2022, see Pub. If you were born before January 2, 1958, you are considered to be age 65 or older at the end of 2022. How do I contact the IRS or get more information? See chapter 5 for discussions on the credit for the elderly or the disabled, the child and dependent care credit, and the earned income credit. What are some of the credits I can claim to reduce my tax? Would it be better for me to claim the standard deduction or itemize my deductions? See Individual Retirement Arrangement Contributions and Deductions in chapter 3. How do I report the amounts I set aside for my IRA? What are some of the items that I can deduct to reduce my income? If I had a gain, is any part of it taxable? See Social Security and Equivalent Railroad Retirement Benefits in chapter 2. How do I report benefits I received from the Social Security Administration or the Railroad Retirement Board? If it is nontaxable, must I still report it? To the right of each question is the location of the answer in this publication. The following is a list of questions you may have about filling out your federal income tax return. You can help bring these children home by looking at the photographs and calling 800-THE-LOST (80) if you recognize a child.
Photographs of missing children selected by the Center may appear in this publication on pages that would otherwise be blank. The Internal Revenue Service is a proud partner with the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children® (NCMEC). See Obtaining social security information, later. For more information, go to SSA.gov/myaccount. Social security beneficiaries may quickly and easily obtain various information from the Social Security Administration’s (SSA’s) website with a my Social Security account, including getting a replacement SSA‐1099 or SSA‐1042S. Your wages are subject to withholding for income tax, social security tax, and Medicare tax even if you are receiving social security benefits. See your income tax return instructions for details.Įmployment tax withholding. It also allows your designee to perform certain actions. This allows the IRS to call the person you identified as your designee to answer any questions that may arise during the processing of your return. You can check the “Yes” box in the Third Party Designee area of your return to authorize the IRS to discuss your return with your preparer, a friend, a family member, or any other person you choose. If there is any underpayment, you are responsible for paying it, plus any interest and penalty that may be due. Remember, however, that you are still responsible for the accuracy of every item entered on your return. If you pay someone to prepare your return, the preparer is required, under the law, to sign the return and fill in the other blanks in the Paid Preparer Use Only area of your return. See the Instructions for Form 1040 for more information. However, the Form 1040-SR has larger text and some helpful tips for older taxpayers.

You can use this form if you are age 65 or older at the end of 2022. Tax Return for Seniors, was introduced in 2019. Individuals who reach age 70½ on January 1, 2022, or later may delay distributions until April 1 of the year following the year in which they turn age 72.įorm 1040-SR. Increase in age for mandatory distributions. The age restriction for contributions to a traditional IRA has been eliminated. Maximum age for traditional IRA contributions. See Form 8915-F, Qualified Disaster Retirement Plan Distributions and Repayments, for more information. Special rules provide for tax-favored withdrawals and repayments from certain retirement plans for taxpayers who suffered economic loss as a result of a qualified disaster.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
